In the ever-evolving world of display technology, TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) LCD displays have emerged as a game-changer, offering superior image quality, faster response times, and enhanced energy efficiency. Understanding the inner workings and components of these remarkable displays is crucial for anyone seeking to harness their full potential. Join us as we delve into the fascinating realm of TFT LCD displays, unraveling their working principles and exploring the intricate components that make them a cut above the rest.
Working Principles of TFT LCD Displays
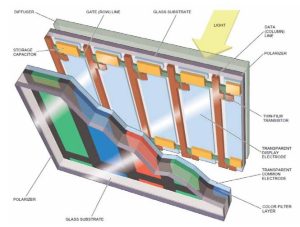
At the heart of TFT LCD displays lies a remarkable technology that combines the power of thin-film transistors with liquid crystal molecules. These displays are composed of two main components: the thin-film transistor (TFT) array and the color filter array.
The TFT array is a layer of transistors made from materials like silicon, meticulously arranged and connected to control circuitry. This circuitry contains drivers that precisely regulate the voltage applied to each transistor, enabling precise control over the display’s pixels.

The color filter array, on the other hand, is a layer containing carefully arranged color filters made from dyes or pigments. These filters are typically arranged in patterns such as RGB (red, green, blue) or CMYK (cyan, magenta, yellow, black), allowing for the reproduction of a wide range of colors.
When a voltage is applied to the TFT array, the transistors activate, allowing light to pass through the liquid crystal layer. This light is then filtered and modulated by the color filter array, resulting in the vibrant and detailed images we see on our screens.

Key Components of a TFT LCD Display Module
While the TFT array and color filter array are the core components, a complete TFT LCD display module incorporates several other essential elements:
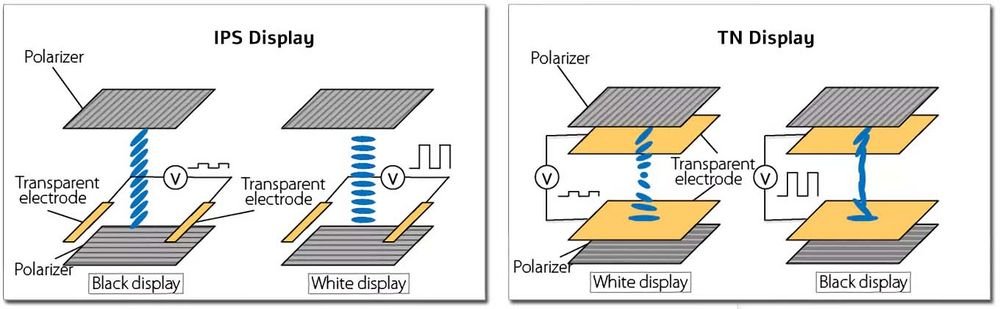
- Liquid Crystal Layer: This layer houses the liquid crystal molecules, typically arranged in patterns like twist nematic (TN), super twisted nematic (STN), or in-plane switching (IPS). These molecules twist and align with the applied electric field, modulating the light passing through.
- Cover Glass: Protecting the delicate display components, the cover glass provides a durable surface for user interaction. TFT LCDs often feature rigid cover glass made from materials like soda-lime or Gorilla Glass, or flexible cover glass for added durability in portable devices.
- Backlight Unit: Illuminating the display, the backlight unit can be composed of various light sources, such as LEDs, electroluminescent panels, or fluorescent lamps, ensuring optimal readability in various lighting conditions.
- Touchscreen (optional): For interactive displays, a touchscreen layer can be integrated, allowing users to directly interact with the screen through pressure-sensitive coatings like capacitive or resistive touchscreens.
- Bezel: Acting as a protective frame, the bezel surrounds and shields the display module from potential damage.
- Driver IC: The driver integrated circuit (IC) is responsible for converting digital signals into analog signals that the TFT LCD panel can interpret and display.
Advantages and Applications of TFT LCD Displays
TFT LCD displays offer numerous advantages over traditional LCDs, including improved image quality, faster response times, lower power consumption, and a thinner, lighter form factor. These benefits have paved the way for their widespread adoption across various industries, including consumer electronics, computing, telecommunications, automotive, and medical fields.