What is a Twisted Nematic LCD?
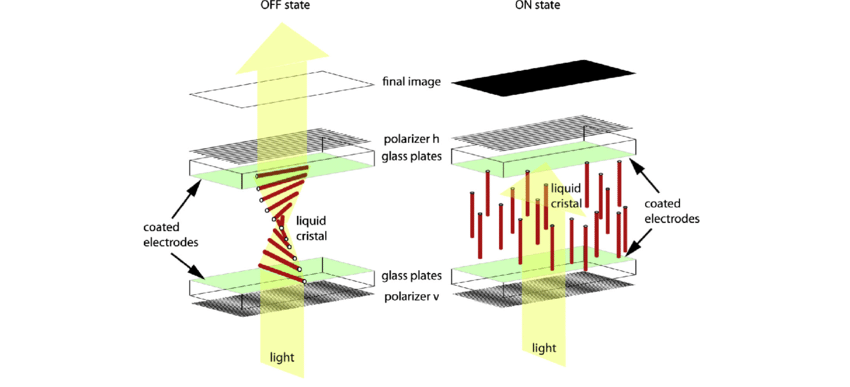
A Twisted Nematic (TN) LCD is a type of liquid crystal display that manipulates light using a twisted arrangement of liquid crystal molecules between two glass substrates. When no voltage is applied, the molecules remain twisted, allowing light to pass through the polarized layers. When voltage is applied, the twist unwinds, blocking the light and creating an image.
Key Features of TN LCDs:
- Fast switching speed
- Simple structure
- Cost-effective manufacturing
- Basic color reproduction
How Does a TN LCD Work?
Here’s a simplified explanation of how a TN LCD operates:
- Polarized Light Entry: Light from a backlight passes through the first polarizing filter.
- Twisted Molecules: Liquid crystals are aligned in a 90-degree twist, guiding the light through.
- Voltage Control: Applying voltage reorients the liquid crystals, disrupting the twist.
- Light Blocking: When twisted alignment is lost, light cannot pass through the second polarizer.
- Image Formation: Varying the voltage controls light passage, producing pixels and colors.
Advantages of Twisted Nematic LCDs
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Fast Response Time | Ideal for motion-rich applications like gaming or industrial panels |
| Low Cost | Easier and cheaper to manufacture than IPS or VA |
| Low Power Consumption | Excellent for battery-powered devices |
| Simple Design | Fewer layers and low complexity compared to advanced LCD types |
Limitations of TN LCD Technology
While TN LCDs are cost-efficient and fast, they have several downsides:
- Narrow Viewing Angles: Image quality degrades from off-center angles.
- Limited Color Accuracy: Not ideal for color-critical applications like photo editing.
- Lower Contrast Ratios: Compared to Vertical Alignment (VA) panels.
TN vs IPS vs VA: A Quick Comparison
| Feature | TN LCD | IPS LCD | VA LCD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Response Time | Very Fast | Moderate | Slow to Moderate |
| Color Accuracy | Low | High | Moderate |
| Viewing Angles | Narrow | Wide | Moderate |
| Contrast Ratio | Moderate | Low to Moderate | High |
| Price | Cheapest | Highest | Mid-range |
Common Applications of Twisted Nematic LCDs
TN LCDs are commonly used in:
- Basic mobile phones and calculators
- Budget laptops and PC monitors
- Gaming displays requiring fast response times
- Industrial and control panels
- Portable gaming devices and digital instruments
Their speed and cost-efficiency make them ideal for high-volume, performance-sensitive, or budget-focused devices.
Conclusion
Twisted Nematic LCDs remain a vital part of the display landscape, especially where speed and cost matter most. Though they may not match the color performance of IPS or the contrast of VA, TN displays provide a reliable, responsive, and affordable solution for many applications.
If you’re choosing an LCD panel for your product, understanding the strengths and trade-offs of TN LCD technology is essential.