What is a TFT LCD Display?
TFT LCD is an active matrix display technology that uses thin-film transistors to improve the performance of liquid crystal displays. It’s commonly used in many low-to-mid-range consumer electronics such as smartphones, tablets, digital cameras, automotive displays, and budget monitors.
- How It Works:
Each pixel in a TFT LCD is controlled by a thin-film transistor. These transistors allow for precise control over the pixels, enabling faster refresh rates and clearer images. This active matrix setup leads to better performance compared to older passive matrix displays. - Key Features:
- Affordability: TFT LCD panels are less expensive to manufacture compared to IPS panels, making them ideal for cost-conscious applications.
- Fast Response Time: TFT LCD panels typically have quick refresh rates, making them well-suited for dynamic content such as video and gaming.
- Decent Color Reproduction: While the color accuracy is good for everyday applications, it is generally not as high as IPS displays.
- Best Use Cases:
TFT LCDs are ideal for entry-level devices where performance, affordability, and energy efficiency are the priorities. Common uses include:- Budget smartphones and tablets
- Automotive displays
- Basic computer monitors
- Portable electronics where battery life is important.
What is an IPS Display?
IPS LCD technology offers an advanced form of LCD that overcomes some of the limitations of TFT LCD, particularly in terms of color accuracy, viewing angles, and brightness. IPS panels are typically found in high-end smartphones, professional monitors, and TVs.
- How It Works:
IPS technology works by aligning the liquid crystals horizontally (in-plane) rather than vertically, which enables superior color consistency and wider viewing angles. - Key Features:
- Superior Color Accuracy: IPS displays deliver richer, more accurate colors, making them ideal for professional environments like graphic design and video editing.
- Wide Viewing Angles: Colors and brightness remain consistent even when viewed from extreme angles, making it perfect for collaborative environments or multi-viewer setups.
- Higher Power Consumption: Due to the more complex structure, IPS LCDs tend to use more power compared to TFT LCDs, which can impact battery life in portable devices.
- Best Use Cases:
IPS LCDs are ideal when color accuracy and consistent viewing angles are essential. Applications include:- Professional design, photo editing, and video production monitors
- Flagship smartphones and premium tablets
- Televisions and high-end displays
- Devices for content creators or those who require precise visual representation.
TFT vs. IPS: A Detailed Comparison
| Aspect | TFT LCD | IPS LCD |
|---|---|---|
| Viewing Angles | Narrower, with noticeable distortion from the side | Wide, colors remain accurate from almost any angle |
| Color Accuracy | Good, but limited compared to IPS | Superior color accuracy and consistency |
| Response Time | Faster, making it suitable for fast-paced content like gaming | Slower response times but still suitable for most professional uses |
| Power Consumption | Lower, beneficial for battery-powered devices | Higher, which can affect battery life |
| Cost | More affordable and budget-friendly | More expensive due to the complex technology |
| Best Applications | Budget devices, automotive displays, basic monitors | High-end smartphones, professional monitors, creative work |
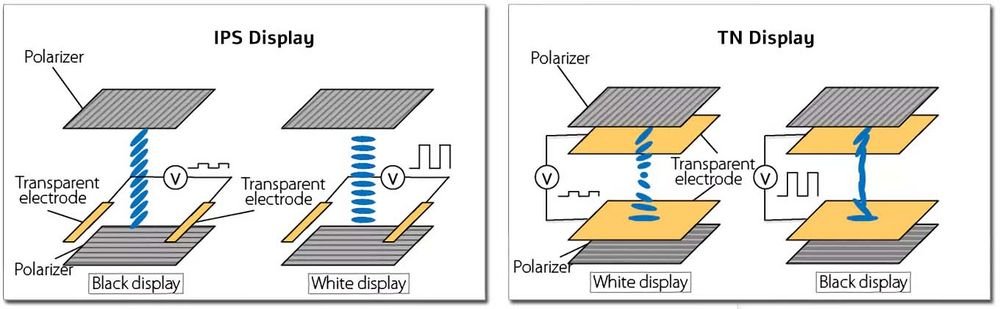
TFT LCD vs. IPS: Which One Should You Choose?
While TFT LCD displays offer several advantages in terms of cost-effectiveness and response time, IPS LCD excels in providing high-quality visuals with better color accuracy and wider viewing angles. Let’s explore when you might want to choose one over the other.

When to Choose TFT LCD
- Budget-Friendly Projects:
If you are developing or purchasing devices with a limited budget, TFT LCD is the ideal solution. Its lower cost makes it a great option for devices where performance is important but cost efficiency is a priority. - Applications with Fast Refresh Rates:
TFT LCDs are ideal for dynamic content where quick response times are critical. This makes them well-suited for applications like:- Gaming
- Fast-moving videos
- Basic smartphones and portable devices
- Energy Efficiency:
For devices that need long battery life, such as smartphones, handheld devices, or wearables, TFT LCDs are a better option due to their lower power consumption.
When to Choose IPS LCD
- Professional Applications:
If you need accurate color reproduction and consistent viewing angles, especially for professional content creation, IPS LCD is the superior choice. Whether you’re editing photos, working on design projects, or producing videos, IPS panels provide the color fidelity necessary for these tasks. - Premium Consumer Devices:
High-end smartphones, tablets, and televisions often use IPS LCDs to provide users with the best visual experience. With wide viewing angles and vibrant colors, IPS displays are ideal for entertainment and media consumption. - Collaborative Work Environments:
IPS LCDs shine in situations where multiple people need to view the screen at the same time, such as in business presentations or collaborative workspaces. The consistency in color and brightness across wide angles ensures everyone gets the same visual experience.
A Final Word
Both TFT LCD and IPS LCD technologies have their place in modern displays. TFT LCDs are ideal for budget-friendly projects, fast-paced applications, and energy-efficient devices. On the other hand, IPS LCDs excel in professional environments where color accuracy, viewing angles, and overall visual quality are critical.
The best display technology for you depends on your specific needs. If you’re working on a cost-conscious project or need a display with quick response times, TFT LCD could be the ideal solution. However, if your priority is color fidelity and wide viewing angles for professional or high-end consumer devices, IPS LCD would be the better choice.
By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of both, you can select the right display technology that aligns with your project’s goals.
